In the last several versions the new features in MS Excel have mostly been cosmetic in nature, but in version 2007 there are many new things. There have been many improvements in apprearance, but Microsoft has in this version also introduced many functional improvements.
Ribbon and Tabs in MS EXCEL
Like the other applications in the Office package, MS Excel has also gotten a new and smarter look. The first thing that catches the eye is that the traditional menu bars and toolbars have been replaced by the new Ribbon. The Ribbon contains Tabs, and each Tab contains buttons for various functions that were previously located int eh menus and toolbars. The Ribbon is far more visual and task-oriented and adapts constantly to the activity you are engaged in. If you have been accustomed to working with menus and toolbars for many ears, it takes a while to get used to the Ribbon, but I mus admit that after some time I have been really pleased with the new system. It appears more coherent, and it is not as messy as the toolbars sometimes tend to be.
Large Workspace
It has always been possible to make large spreadsheets in Excel. In previous versions you could have 65,536 Rows, and 256 Columns. this made for pretty large spreadsheets, but you have better sit down for this: In Excel 2007, you have up to 10,48,576 rows and 16384 columns.
More Colors in MS EXCEL
It previous versions you had only a few colors to choose from when you had to put background colour in the cells. Now you can choose between 16 Million different colors. You can also create colour transitions inside the cells. It gives you unprecedented opportunities to create worksheets that look nice and inviting.
Color Themes and Styles
Now you can use predefined colour themes in MS Excel. this feature is known from Word and Power Point, where the programs help you format your entire document, so everything appears smooth and harmonious. this is also possible in Excel now. If you make charts, they will automatically be consistent with the colour theme that is selected.
Improved Conditional Formatting
The Conditional Formatting functions has been significantly improved. there are more opportunities for highlighting of, for example, Top 10 and it is possible to colour the cells according to cell value.
More and Better Looking Charts
Excel 2007 has no new basic hart types, but there are now more variations of existing ones. Formatting has been improved, and you can, for example, add soft shadows behind your columns, which gives a nice effect. If you do not choose the colors in a chart yourself, the colors in the spreadsheet color theme will be automatically applied, so everything appears harmoniously.
New File Format
Excel uses a new file format which is not compatible with earlier versions. If you have worked with the program before, you will know that the file name ends in Xls. In Excel 2007 the file name ends with “.Xlsx” . For the technically minded, I can reveal that it is an XML based format, which gives smaller file sizes and better opportunities for integration with other programs. You can still save your spreadsheets in the old format, but be aware that some functionality may be lost.
Where can I find the Old Buttons
If you are familiar with older versions of Excel, you will probable have trouble finding some of the old features. This is obviously because the menu bar and toolbars have been replaced with the “Ribbon”. It might be a little confusing, but I’ll try to list the main functions, so you can find them quickly. ew, Ope, Save, Save As and Close are located in the Office Button at the top left. The Save feature is also available as standard in the Quick Access Toolbar, located just to the right of the Office Button. Preview is also available in the Office Button under menu item Print.
The Drawing toolbar no longer exists. It has been replaced by the Shapes and Smart Art buttons under the Insert tab in the Ribbon.
The Insert symbol is also located in the Ribbon under the Insert tab. this button is simply called Symbol. Normal view and Page Break preview are there as small buttons at the bottom right corner of the screen.
The Insert functions have been replaced by the Formulas Tab in the ribbon. this is a clear improvement, but if you prefer the old dialog box, you can get it by clicking of FX on the formula bar.
First Look at Excel
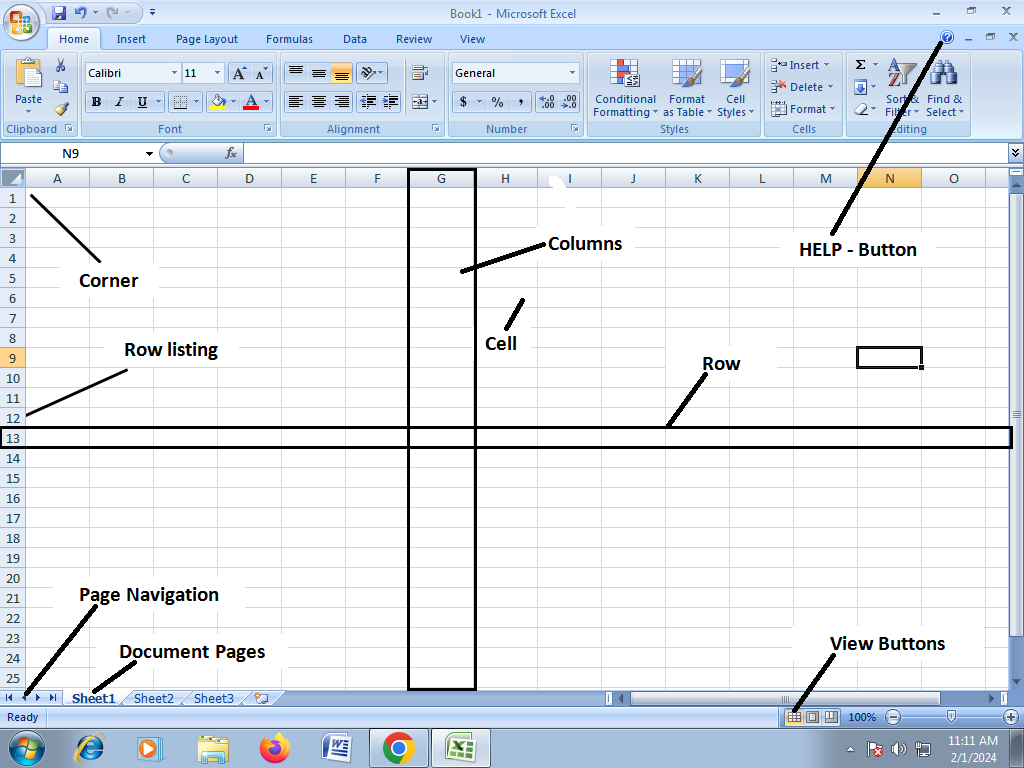
The Screen and its Elements
When you start Excel, you will automatically start in a new, blank workbook
Workbooks and Spreadsheets
and ordinary Excel file is called a “Workbook” and can contain different things. The most important thing is that it can contain worksheets, but it may also contain chart sheets and sheets and small programs that you can do yourself. the most important thing is to be aware that an Excel file is not necessarily just a spreadsheet but a workbook that can contain many spreadsheets and charts.



